Understanding Egyptian Corporate Tax: Protect Your Business and Avoid the Unexpected


Corporate taxation is one of the essential financial obligations businesses must adhere to when operating in Egypt. Whether a multinational corporation, a small local enterprise, or a foreign branch, understanding corporate tax laws is vital for staying compliant with legal requirements. In this post, we will explore the fundamentals of corporate tax in Egypt, including who needs to pay it, applicable tax rates, deductions, filing requirements, and common mistakes to avoid.
Corporate tax is a levy imposed on the profits of companies that operate within a country’s borders. In Egypt, all companies that generate income, whether Egyptian-owned or foreign branches, are subject to corporate taxation. The Egyptian tax system requires businesses, whether large enterprises or small local firms, to pay taxes on their annual profits. The system also applies to foreign companies with branches or operations in Egypt, ensuring that all businesses contributing to the local economy are held accountable for their tax obligations.
Corporate tax is crucial for supporting the government’s ability to fund public services and infrastructure projects, making it a central component of Egypt’s broader economic structure.
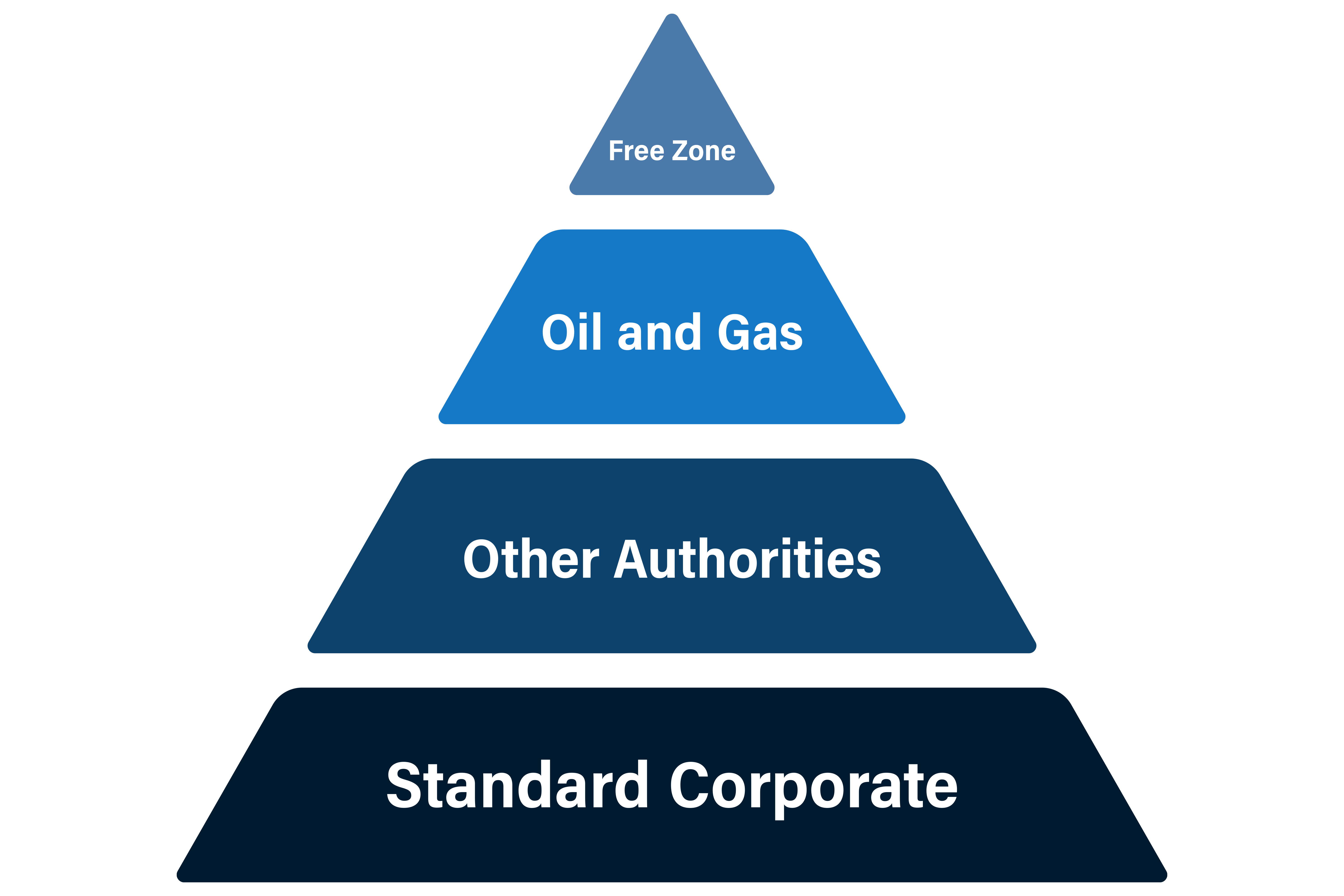
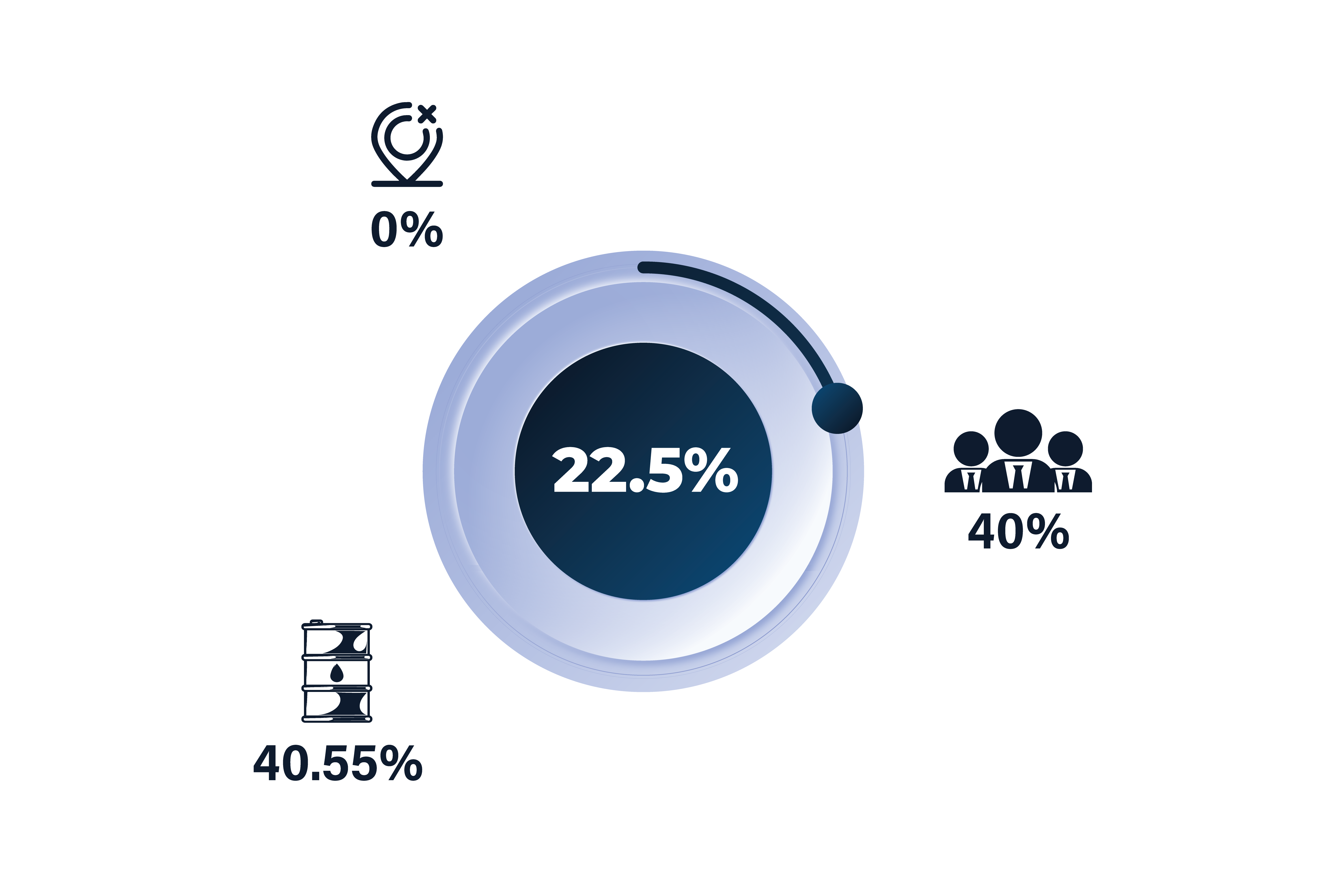
The general corporate tax rate in Egypt currently stands at 22.5%, making it one of the region’s competitive rates for businesses. However, there are specific sectors where tax rates may differ. For instance, the oil and gas industry, which has long been a cornerstone of Egypt’s economy, is subject to higher tax rates, with some companies facing rates of up to 40%. Similarly, businesses involved in exploration and production may also encounter different taxation structures.
Despite these variations, the flat 22.5% rate applies to most businesses, regardless of their size or the industry they operate in. This stability helps make Egypt an attractive market for foreign investment and local entrepreneurship alike.
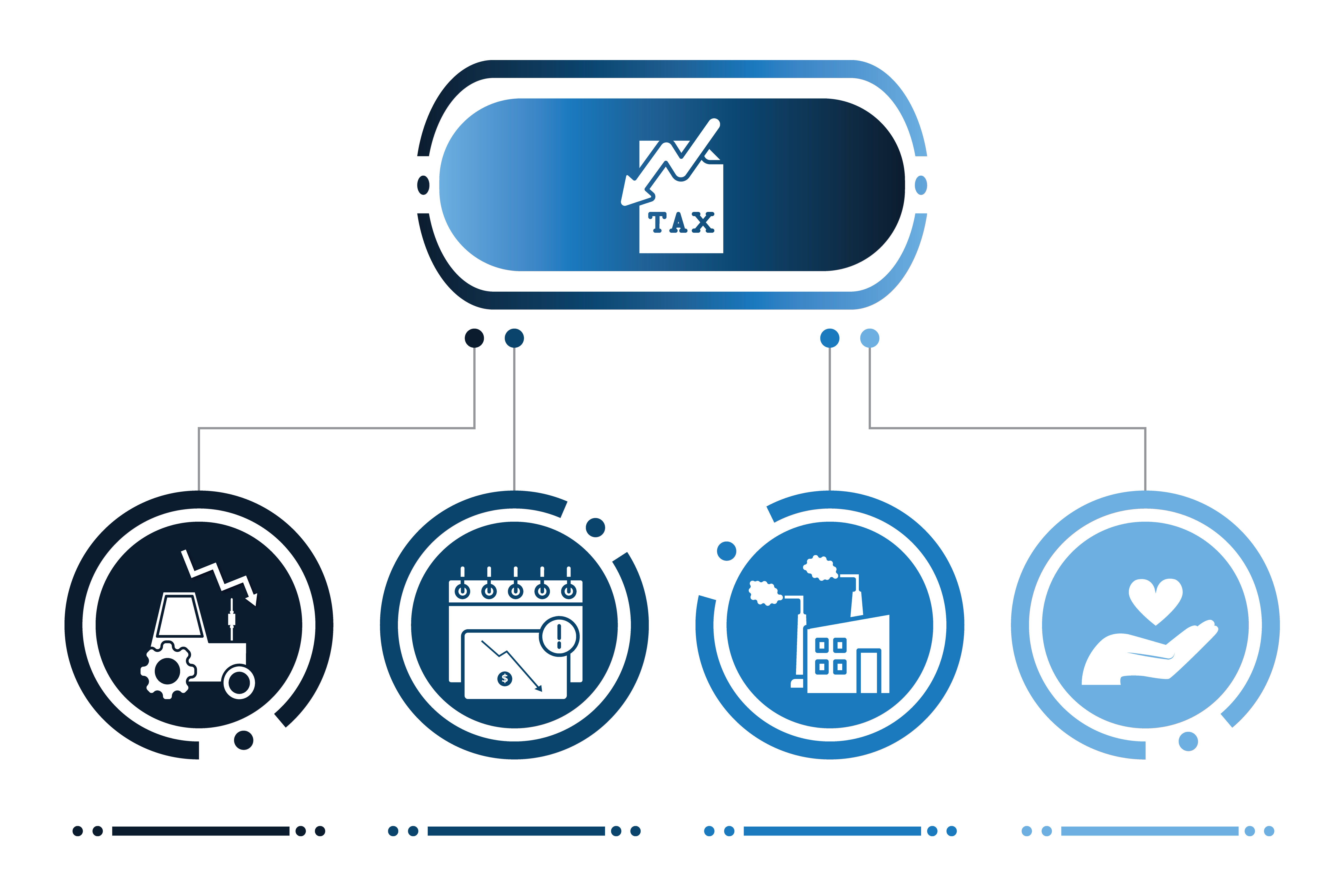
Egypt’s tax system allows for a range of deductions and allowances that can help reduce a company’s overall tax liability. Some of the most common deductions include:
Understanding and effectively utilizing these deductions is crucial for optimizing your company’s tax strategy and ensuring compliance with Egyptian tax laws.
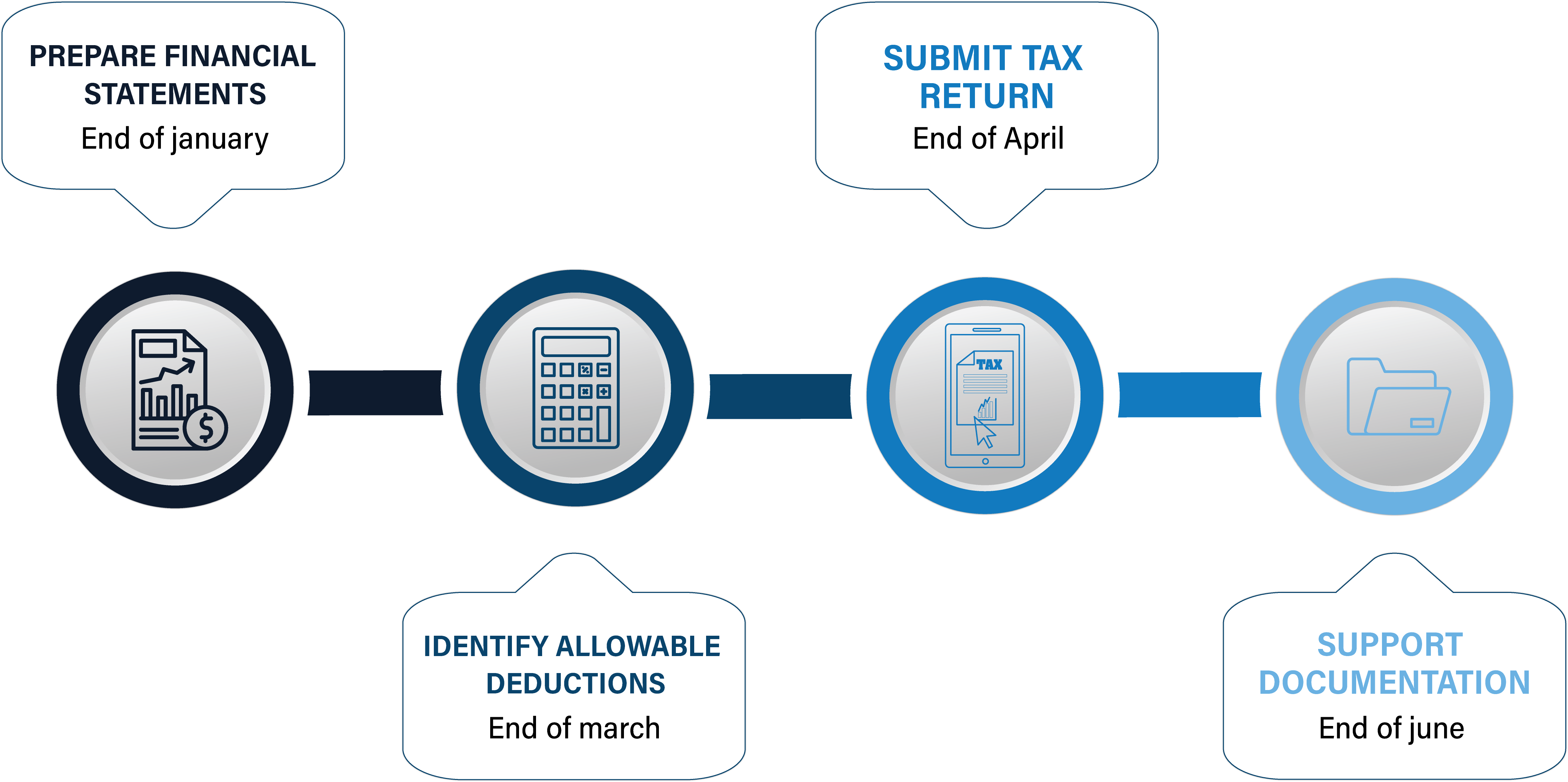
Corporate tax returns in Egypt must be filed annually, with the deadline typically set at the end of April following the tax year. Companies must submit their tax returns electronically, along with all necessary documentation to substantiate their reported income, expenses, and deductions. Required documents may include financial statements, proof of income, and records of any deductions claimed.
Failure to file taxes on time or provide accurate documentation can result in penalties, which may include fines or increased scrutiny from tax authorities. It’s critical for businesses to stay ahead of filing deadlines and ensure that all financial records are properly maintained throughout the year.
Here’s a quick look at the corporate tax filing process:
Even the most experienced businesses can make errors when filing their corporate taxes. Here are some of the most common mistakes and how to avoid them:
By avoiding these common pitfalls, businesses can ensure they remain in good standing with the Egyptian Tax Authority and minimize their tax liability effectively.
Corporate taxation in Egypt is a key component of doing business in the country, and understanding its fundamentals is critical for every company, big or small. By staying informed about the corporate tax rate, making use of available deductions, and adhering to proper filing requirements, businesses can ensure they remain compliant with the law while optimizing their tax strategy.
While taxes can often be a complex and intimidating aspect of running a business, proper planning and awareness of tax regulations can go a long way in ensuring smooth financial operations. Keep your records accurate, stay updated on tax laws, and approach the filing process methodically to avoid potential pitfalls.
Last Update: Mon, Mar 9, 2026 9:25 PM
Total Views: 32050